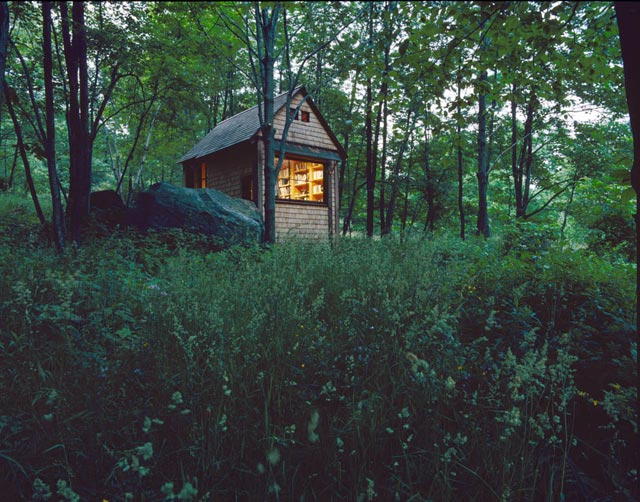
I am currently leading an adult learning group on the theme of Art, Beauty, and Transcendence. Some wonderful observations were offered by my fellow learners at our first session. After inviting our participants to introduce themselves and share a recollection of a memorable encounter with Beauty, I provided a discussion prompt: Is Beauty essential, or is it a luxury? We seemed to share a consensus that it is an essential part of our lives. And then a participant said, “I find Beauty everywhere!”
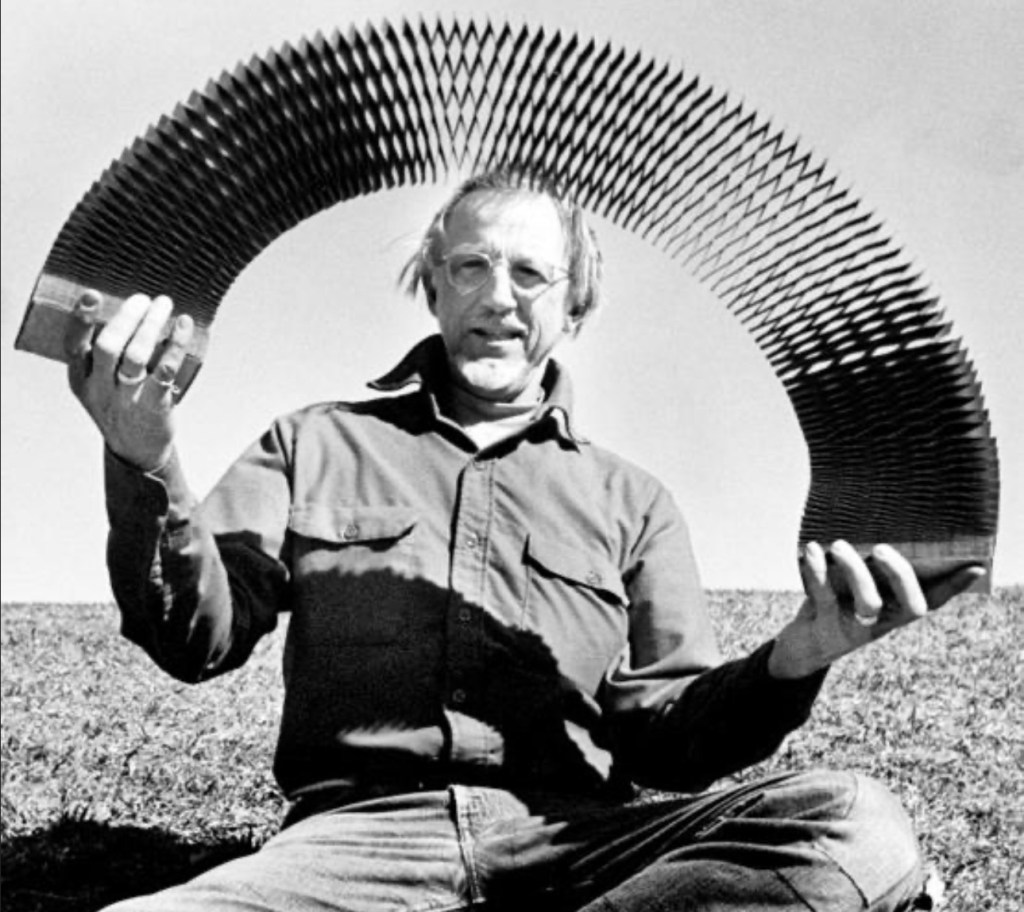
Hearing this, I thought of Reinhold Marxhausen, a remarkable artist and teacher who had a vision for how we all might approach our daily encounter with our ordinary, everyday circumstances. His captivating approach to life impacted many people beyond the classroom and studio – me among them. Here is one way to sum up the vision he shared with others: “Beauty can be found everywhere – you just need to look for it!” So simple is this message that I am sure it has more often been dismissed than pursued as a practice.

Reinhold Marxhausen did not just send folks away to try this on their own; it became his mission to show people how to do it. This is made clear in a video of his appearance on the David Letterman show, with the interviewer doing a great job of giving rein to the artist’s creative spark and communicative abilities. Marxhausen‘s Letterman show appearance can be found on YouTube.

I continue to be intrigued by what Marxhausen’s abiding belief implies- that Beauty is found, in addition to how we are led to it by others, or more simply that it is something we just designate for ourselves. These are three different ways that we might encounter Beauty as a feature in our lives, if not as something even more profound for how we view our lives and the world.
Readers of my posts in this space will be familiar with the parallel I have discerned between the three principal forms of jurisprudence (or theories about the source of Law, and three main sources for our concept of the Good in our understanding of ethics. Found, received, and or made, are the three terms I use to summarize these three approaches to where Law comes from, as well as for sources of our notion(s) of the Good. In offering this summary, I do not exclude the possibility of other sources for Law and or the Good.
More expansively, according to the first view (1), Law and the Good are entities written into the structure of ‘reality.’ As such, these things are ‘there’ for us to find. Another possibility (2), sees Law and the Good as worthy principles we receive from those who have come before us, as things commended to us by longstanding traditions. We sometimes describe them as things that have stood the test of time. A third possibility (3) is that Law as well as the Good are sets of principles about which we come to agreement, or decide upon and enact for ourselves and others. Hence they are things of our crafting, things that we ‘make,’ as we project our preferences outward upon the world. Formal labels for these three approaches include natural law or Creation order (1), historicism or common law (2), and positivism or civil law (3).
Here is something I want to stress: we are rarely consistent in how we think, perceive, and understand important aspects of our lives. We should therefore anticipate an overlap between these several conceptual categories for how we think about Law and about ethics. In other words, a ‘both-and’ approach regarding them may be much more appropriate than seeing them in an ‘either/or’ way.
So, is Beauty amenable to a similar analysis? I think it is. For Beauty is found (1); we also discern Beauty in the company of others and through their guidance (2); and we surely fashion notions about what is beautiful through personal preference and decision-making (3).
If you believe you have ‘found’ Beauty at some or at many points in your life experience, would you be content to accept the proposition that your encounter with Beauty is actually reducible to the social impact of others upon your perception, and or that it was and is merely the result of personal preference and choice?