If reading this by email, please tap the title at the top to open your browser for the best experience. Then, clicking individual pictures will reveal higher resolution images.
With the Western art of Tom Gilleon, we find another example of a skilled painter trained in the practice of traditional representational painting, whose work has morphed over the years to incorporate some features of Modern Art that are commonly associated with post-World War II American painting and printmaking. Viewers familiar with Gilleon’s paintings will notice his repetitive motif of portraying tipis on the prairie, rendered in multiple ways with varying color combinations. Yet, and in a way reminiscent of Andy Warhol’s numerous print series, the compositional elements of many of Gilleon’s paintings are often the same.
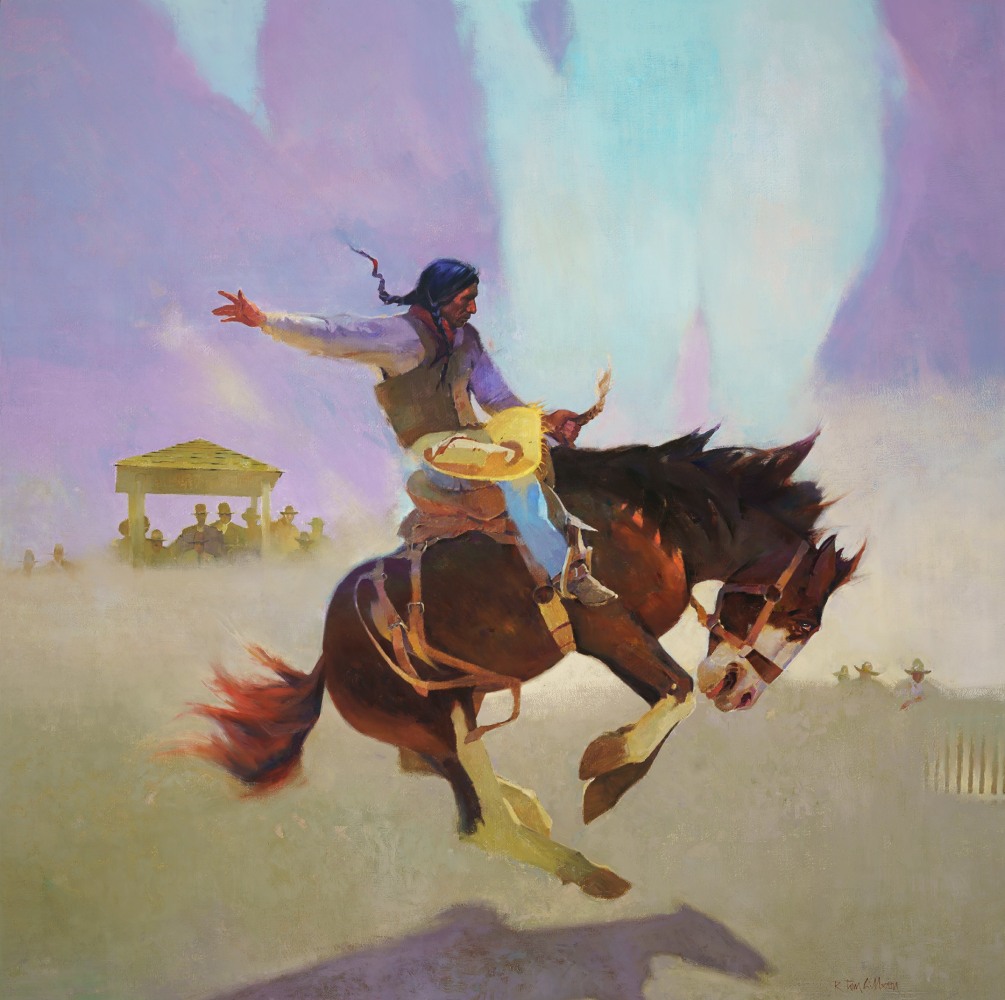
One potential criticism of so-called Modern Art, heard less frequently now, is that many viewers find examples of the genre to be simplistic, perhaps lacking in creativity, and potentially the product of less talented artists. I have addressed that observation before, especially with reference to the work of Jackson Pollock as well as James M. Whistler. In my view, elements of image composition, color choice, and the placement of the colors selected within a given work of art, as well as how color is applied, represent choices made by painters the sophistication of which is easy to overlook. In the case of Tom Gilleon, the artist’s bone fides as a skilled painter can easily be established. Note the following examples of his more traditional representational work.
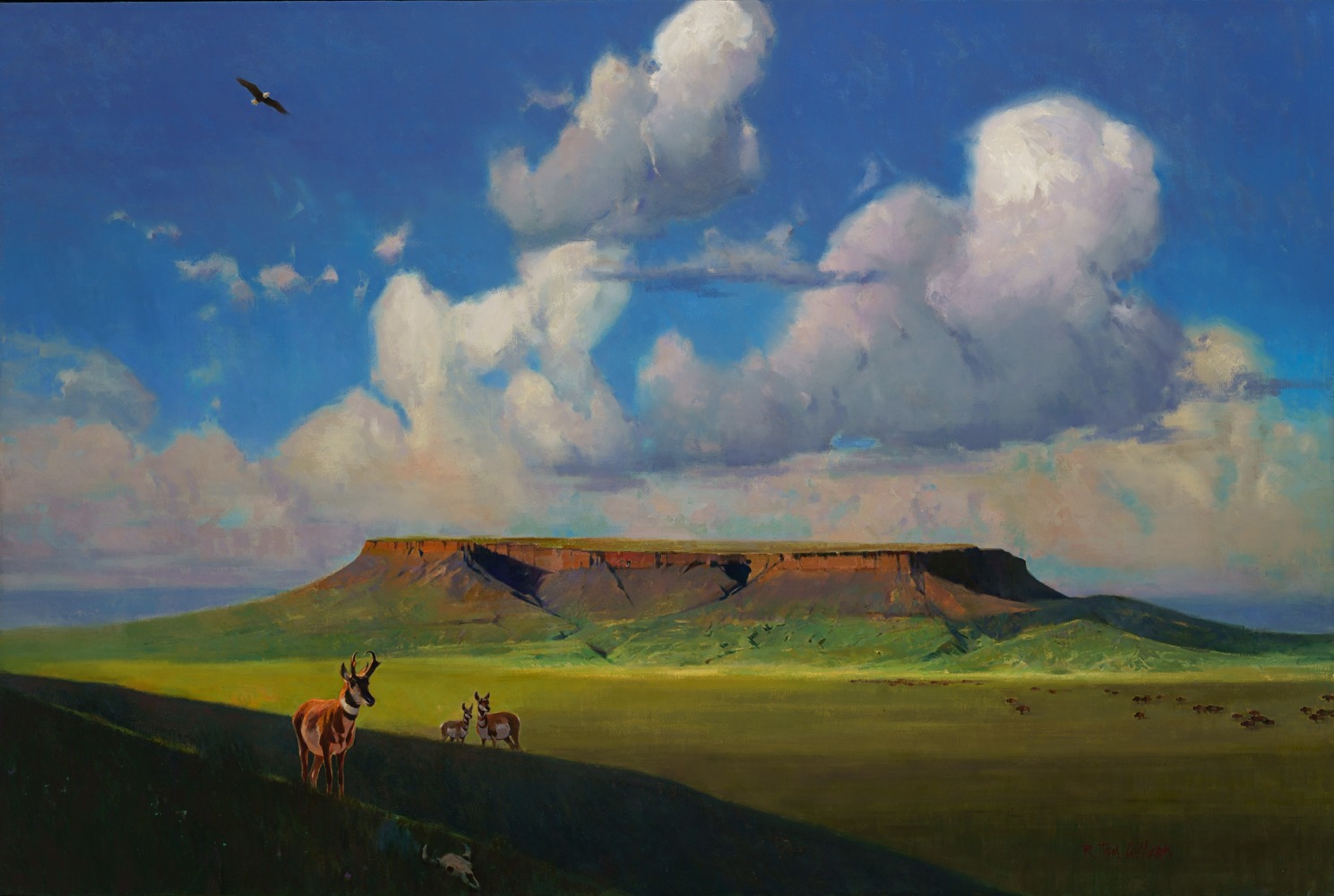
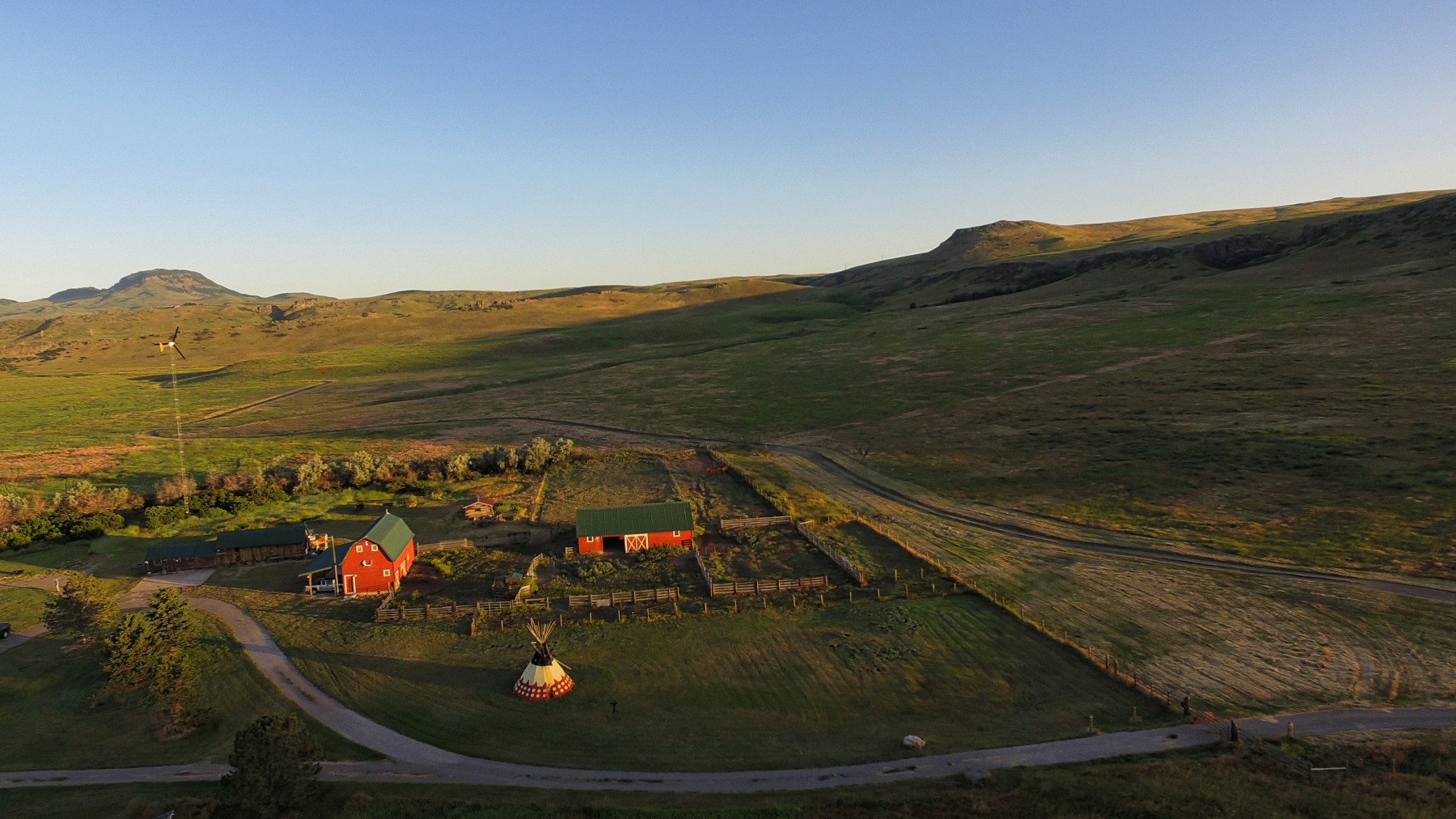
The image shown immediately above, based on the mesa visible from Gilleon’s studio, provides a reference point for observing the range of his interests as a painter. The same view, featuring much less detail, can be seen in his image below.
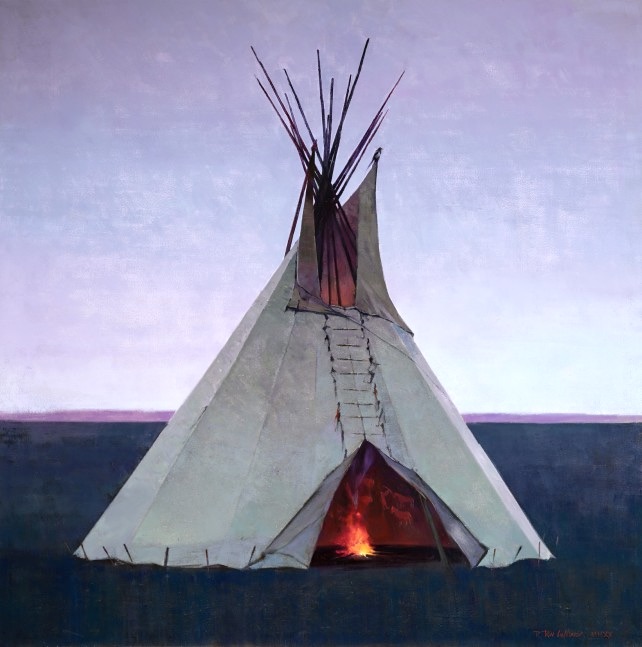
While fully capable of portraying a Native American tipi encampment with sensitivity to its geographical and historical contexts, Gilleon over time has come to focus his work less strictly on the representation of scenes he has observed, and has moved toward an exploration of particular elements within those scenes. This has allowed him to focus more directly upon picture composition and the exploration of color. This broadening of his work as an artist can be seen in a number of images shown below. First, we observe two images that are more clearly dependent on physical observation of – or extrapolation from – specific contexts on particular occasions.
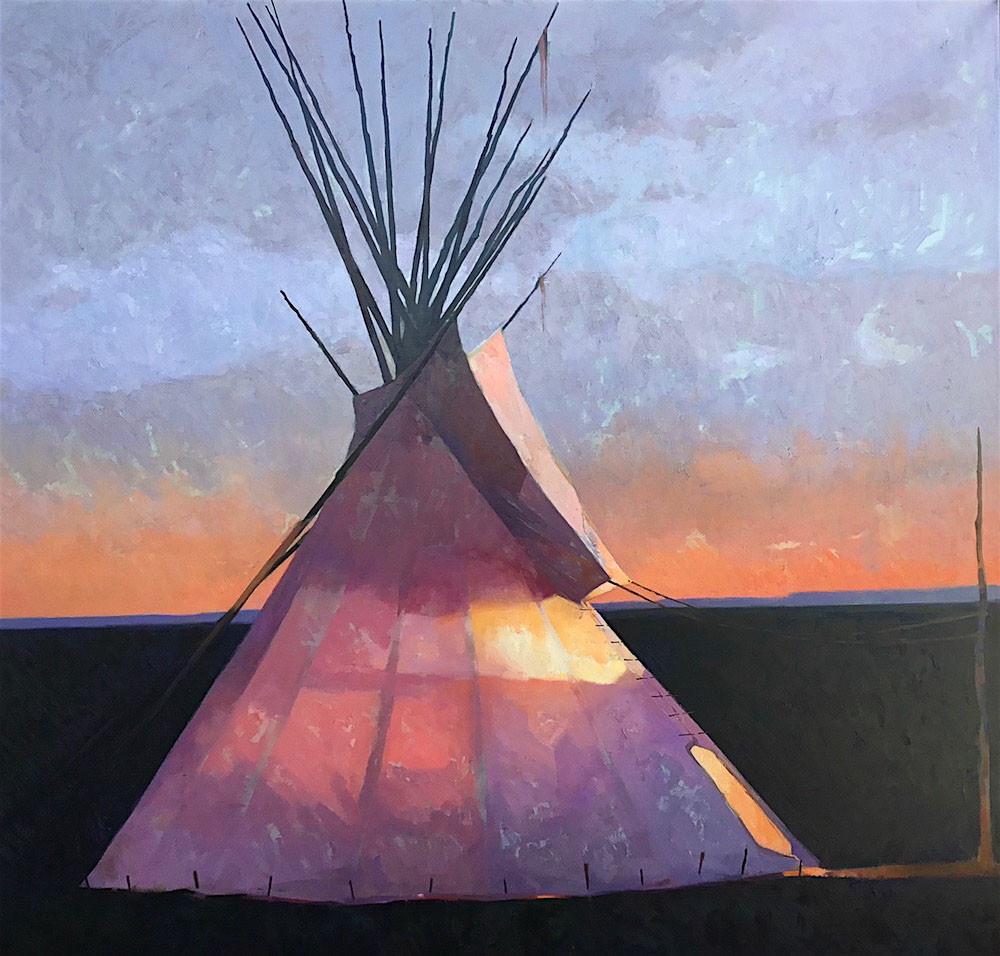
In the above two paintings, we can appreciate the artist’s skillful attention to such details as the nature of the weather, varying daylight conditions and the way they are reflected on the surface of water, and how he portrays features of the physical terrain such as a mountainside in evening light, or a mountain range obscured by a rain shower. But then, we can go on to enjoy the artist’s greater attention to the tipis themselves, and to how a common compositional element that is repeated with little variation over the course of a number of images, can give rise to a marvelous series of explorations of differing light conditions. These explorations include renderings of the effects of light both within and around the tipis that he portrays, as well as its effect upon the surfaces of those structures and the terrain in which they sit.
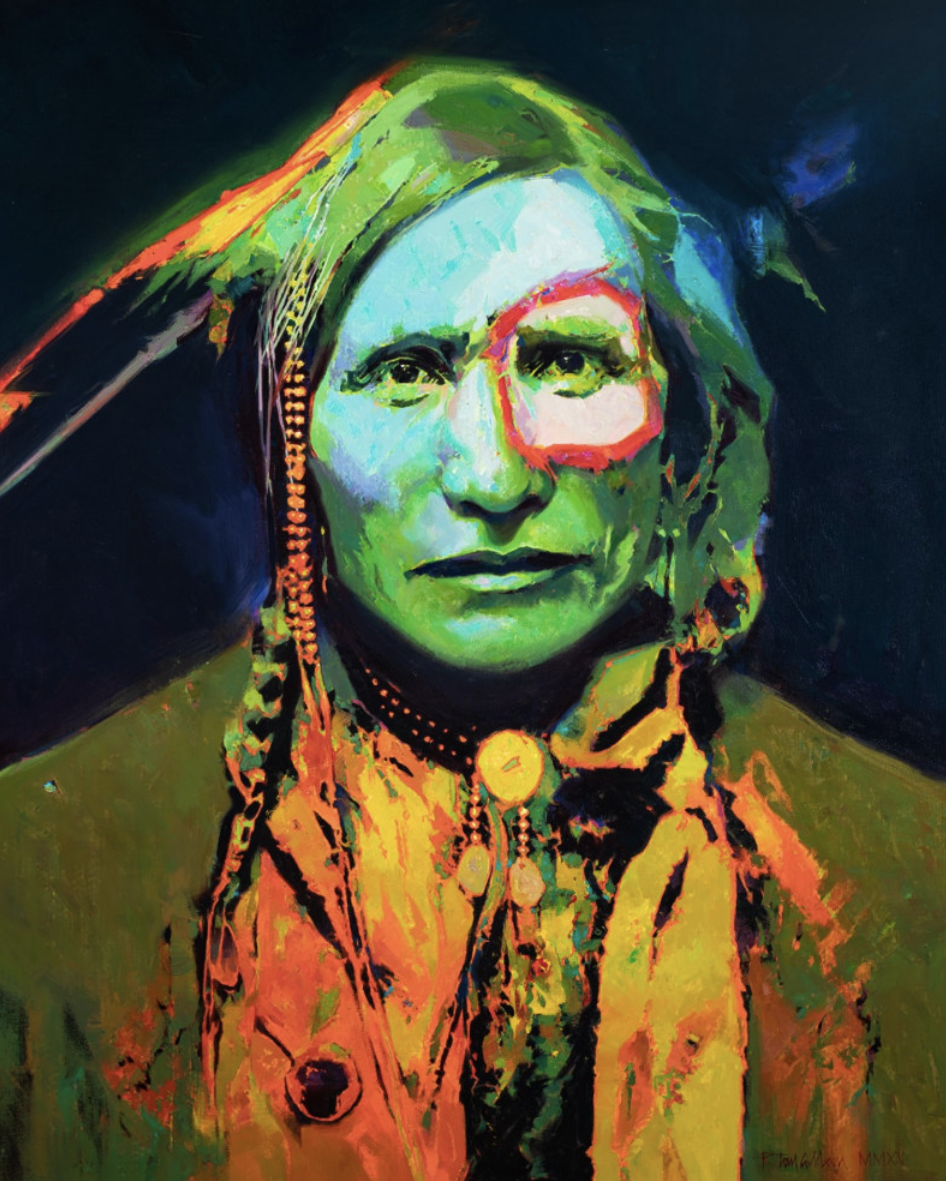
The latter image, so much like the ones shown above it with regard to image composition, as well as attention to color and light, is of interest because of the very subtle shift evident in the directional location of the tipi’s entrance, and the lone bare pole in the far righthand side of the painting. In this same image, the artist has felt free to move away from reproducing a historically accurate representation of various ways that particular Native American communities would apply decoration to the tipi’s surface, so as to be in a better position to attend to the abstract components of color and light in themselves.
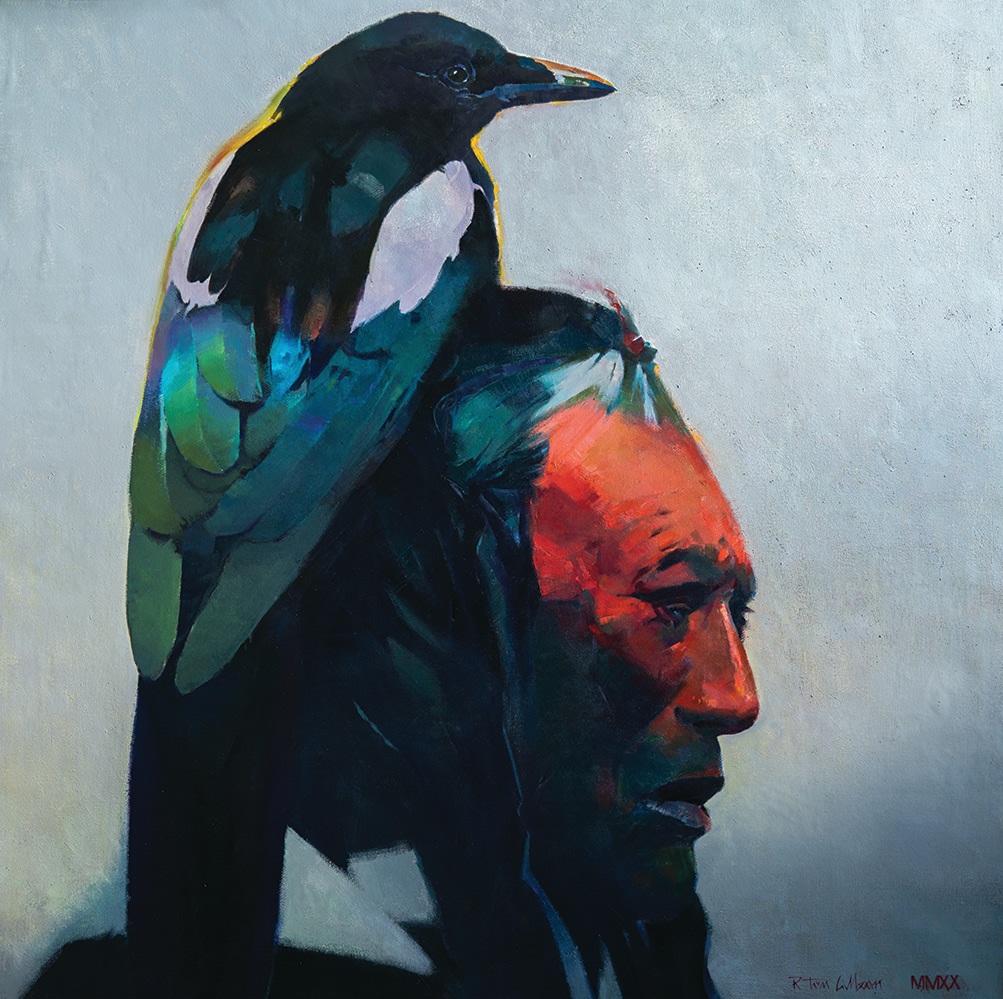
At the outset, I alluded to Gilleon’s incorporation of aspects of painting commonly associated with the work of Abstract Expressionists as well as those whose work became associated with the label, Pop Art. The following images provide good examples of Gilleon’s willingness and ability to work beyond the parameters of more traditional landscape and portrait painting.
The artist (below) in his studio, with his view of the flat-topped mesa in the distance
The artist’s studio on his Montana ranch, with a tipi in the foreground