In the summer of 1974, I left my Massachusetts prep school as one of the few graduates not intending to go on to college. I moved to Manhattan in a youthfully naive venture to try and replicate an aspect of the life of my hero, Frank Lloyd Wright. I wanted to follow his career path of eventually obtaining architectural licensing through practicing in the field, something that was and may still be possible.
Unfortunately, as a career move this was at an improvident time, largely due to what was then called “the oil crisis,” and its effect upon the economy. No architectural office was hiring beginning draftsmen, and some were taking on licensed architects to do the kind of basic drafting work for which I wanted to be hired. The former Frank Lloyd Wright associate, Edgar Tafel, was most gracious in allowing me to come to his New York City office for an interview and then by how he tolerantly responded to my youthful exuberance and evident lack of preparedness for the work. Philip Johnson was less patient with me. When I managed somehow to reach him by phone, he said, “Look – I don’t do the hiring around here. Talk to my associate!”
I had found a room a block and a half from the Cathedral of St. John the Divine, which was a prominent local landmark and soon became a welcome place to visit. Only years later did I discover that the house in which I had been able to rent my room, the former Alpha Delta Phi fraternity house, on 114th St, opposite the Columbia University Library, was where Thomas Merton had lived when he was a student there.
I would walk over to St. John’s, an alluring place to stop and rest. Now, at this point in my life, I would say it was ‘to pray.’ But I would not have said that then. Yet, as one beautiful phrase in The Book of Common Prayer Catechism puts it, “Prayer is responding to God.” Those are profound words. If taken seriously, we can recognize how many, many people in this world ‘respond to God,’ quite spontaneously and quite naturally – and aside from doctrine or ritual.
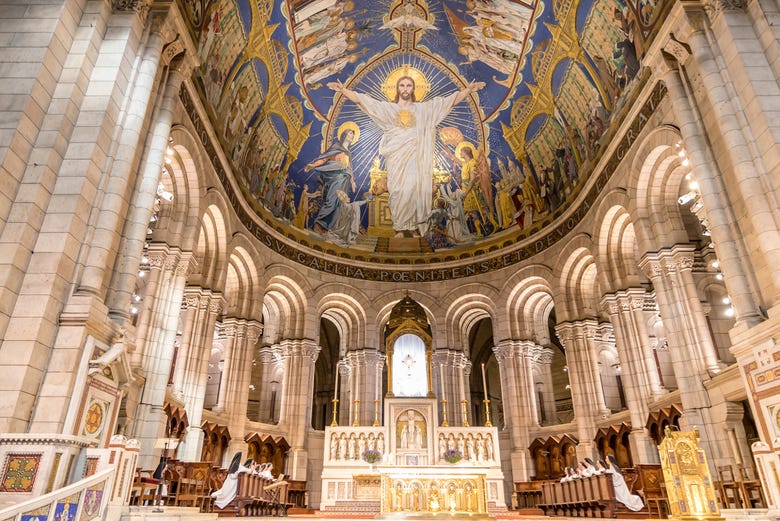
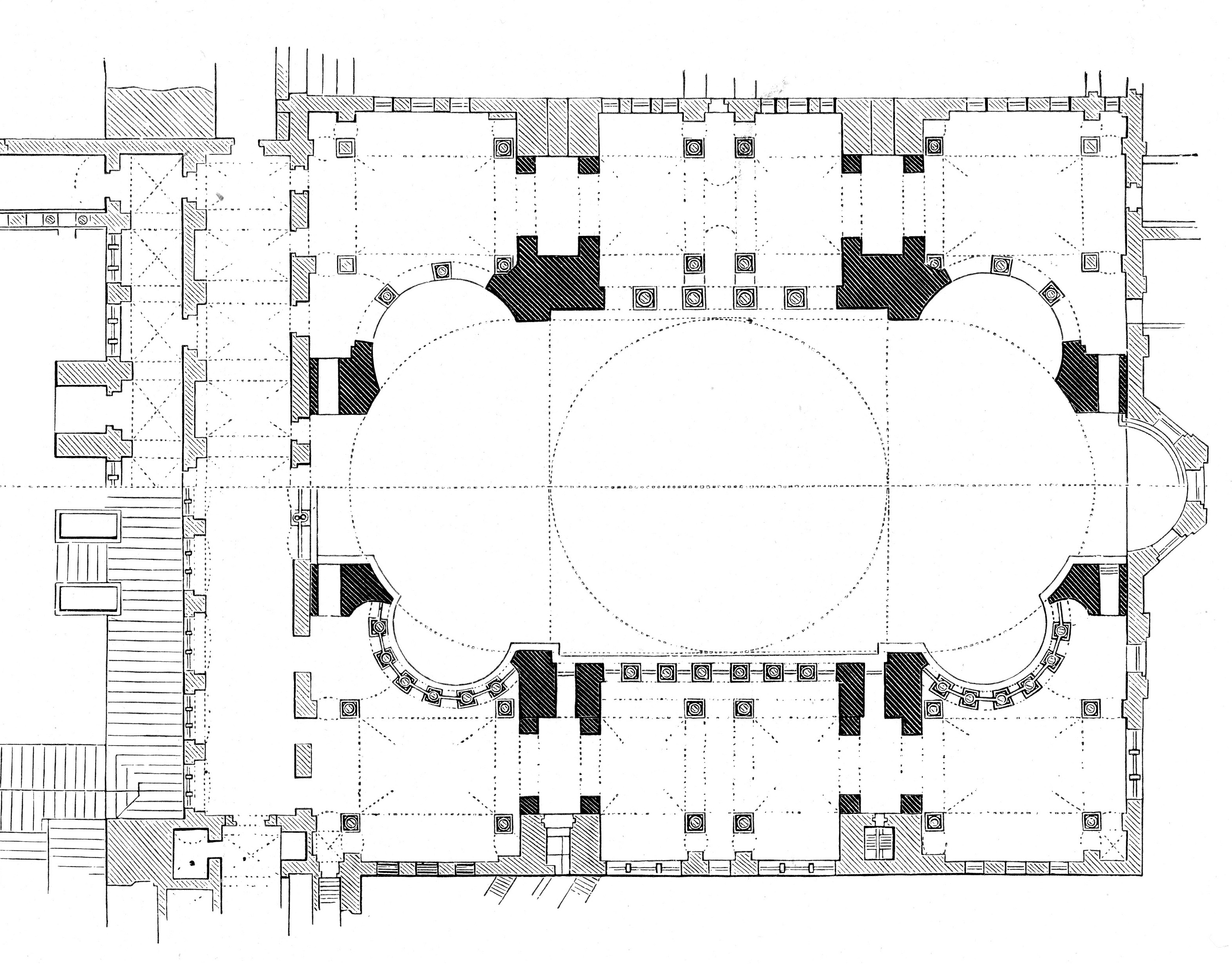
The magnificent space and architectural achievement of the unfinished cathedral of St. John the Divine was a profoundly converting space for me, in ways I did not realize then, and in ways that would not really make sense to me until much later.
Drawn to this place, absorbed with my intuitions about its architecture, and visiting frequently with inquiries, I volunteered to become a docent, a kind of tour guide for visitors before places like this cathedral became commercially oriented, leading to the charging of fees and the like. In the process of my time as a guide, I learned many arcane and obscure things, among them the size and height of the granite columns surrounding the main altar (54’ tall, 6’ in diameter); the number and architecturally significant variations among the chapels adjacent to the ambulatory surrounding the apse that encloses the high altar; as well as significant features of other side chapels in addition to the crypt.
If you had asked me then about the nature of my interest in that building, I would have said it was purely of architectural significance. Ask me now and I will tell you that I was seeking a closer experience of what St John the Divine shares with us in his Gospel. I was – as we say in a paradoxical way – unconsciously looking for God. But what I was really looking for, as we all do, is the experience of being found… and of feeling found, by God.
I think it is also providential that my year in New York, and the brief time I served as an occasional volunteer guide at the Cathedral, was when Canon Edward West was Sub-Dean, and Madeleine L’Engle was officially the cathedral librarian. I may have had only passing contact with either of them, but both were exemplars of how the arts may draw people into a more direct experience of what our Christian faith is all about. The Cathedral of St. John the Divine has represented this vision and value for decades.
Where St. John the Divine as a building nurtured my nascent spiritual awareness, the Gospel given to us through St. John the Divine, and the hymn-poems in his Revelation, have been for me a key, a doorway, and a beckoning gateway into a greater fullness of life.