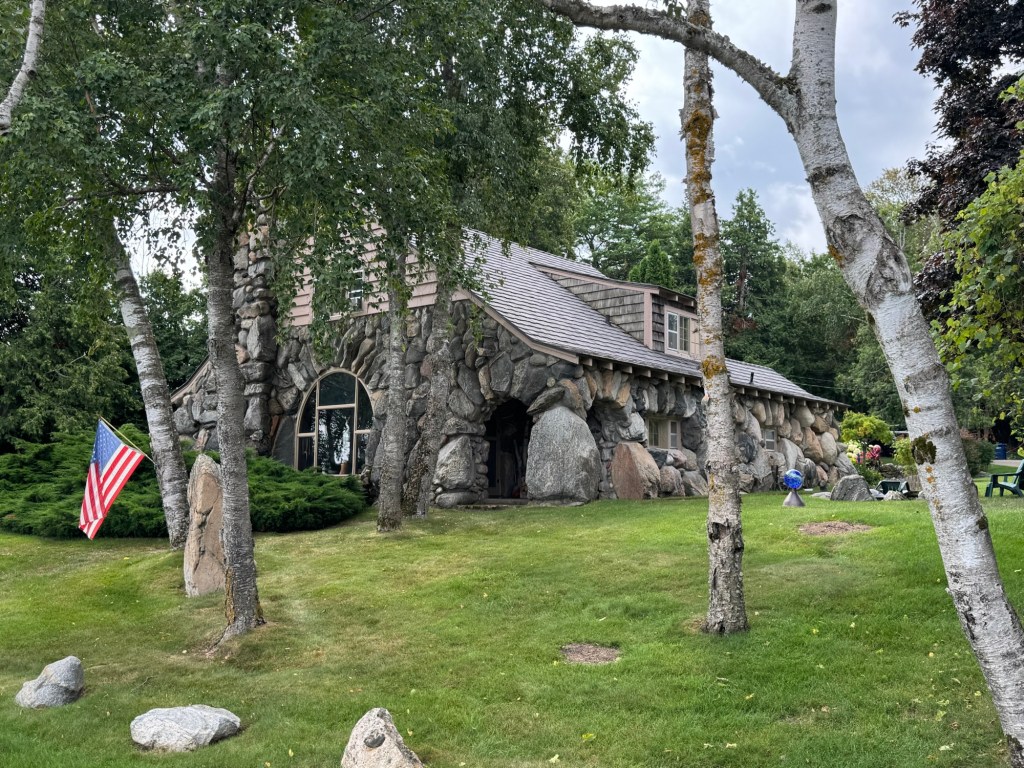Frank Lloyd Wright and Philip Johnson number among the most well known American architects of the 20th century. Both are remembered for their many commissions by others, for buildings constructed both in the United States and overseas. Notably, each of these men designed a house for himself and each reflects something of the respective architect’s vision for an ideal domestic building. The results differ dramatically and beg for some explanation, especially in the case of Philip Johnson’s Glass House.

To help appreciate the theoretical basis for these vastly differing houses, I find it helpful to draw upon a distinction made by the earthscape artist, Andres Amador (featured in a prior post). Speaking about his temporary compositions ‘sketched’ upon large stretches of beach areas at low tide, Amador refers to some of his works as “geometric” and others as “organic.” The geometric works display a quality readily suggested by the name for them, and reflect Amador’s training in math as an engineer. The organic works arise, he says, from the site, and he suggests that these pieces communicate their form to him. For me, Amador’s distinction can also be referred to as the distinction between pattern that is ‘received,’ as compared with pattern that is ‘imposed.’
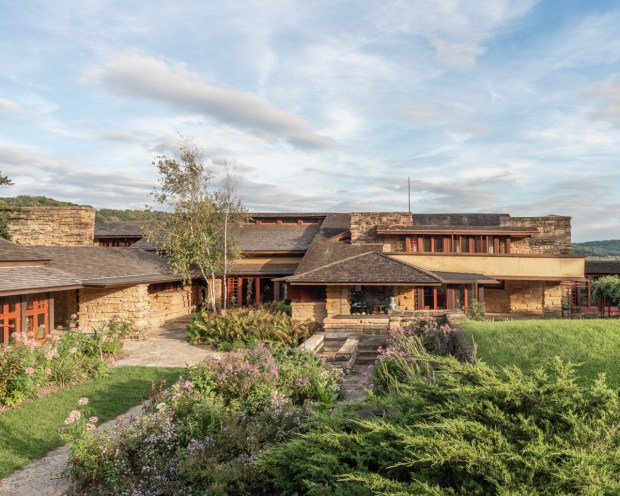
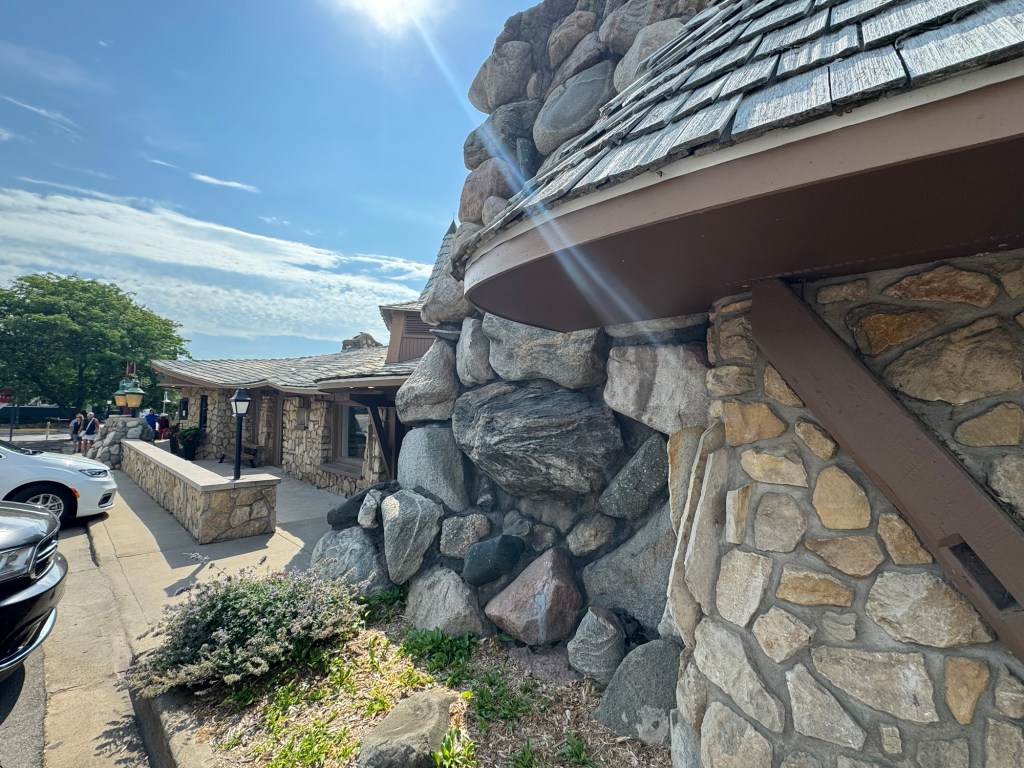
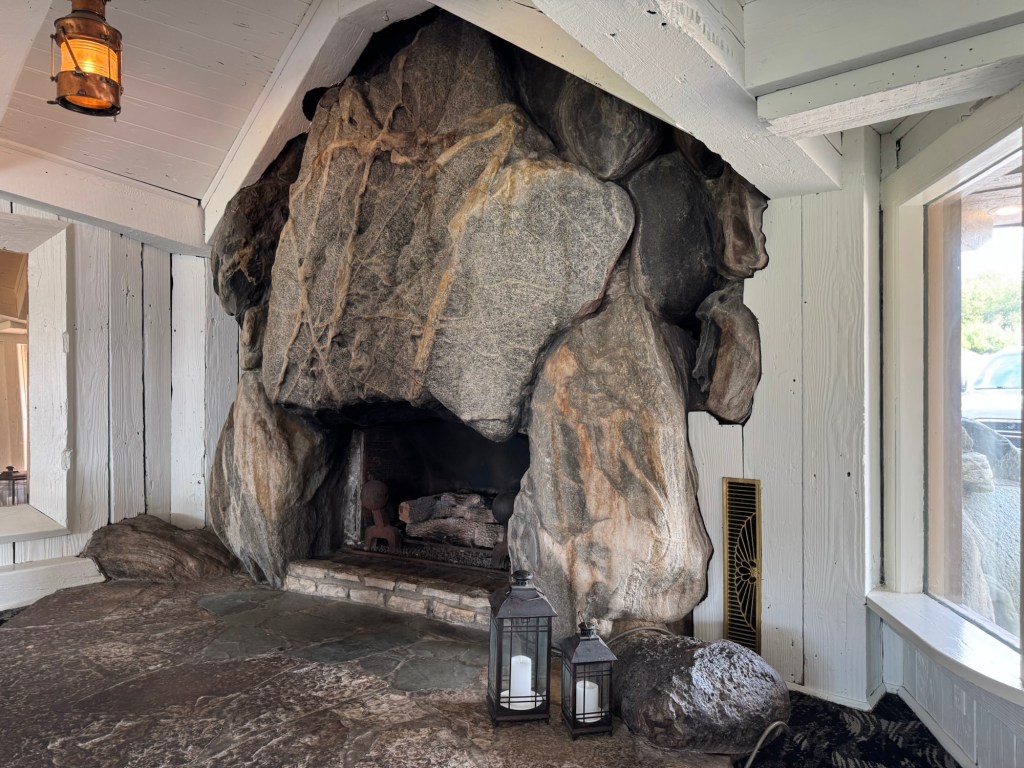
Amador’s distinction between the organic patterns that arise from the site, and the geometric patterns that result from conceptual pre-planning, can assist us in perceiving some themes that are implied by the architectural designs produced by Wright and Johnson for their homes. In the case of Wright, he built Taliesin on family property in Spring Green, Wisconsin, in an area where he grew up and with which he had a deep attachment. Like much of his other work, Wright wanted Taliesin to appear as if it was an extension of the materials and features of the site in which it is placed, being an ‘organic’ development of a human habitation within a natural setting. Wright’s intent is evident in the way that the horizontal bands of stucco on the facade, as well as of the limestone in the foundation and walls of the building, parallel and mirror the layers of stone found on the site.


While Philip Johnson’s architectural practice was located in New York City, he planned to build a house for himself and weekend guests in nearby New Canaan, Connecticut. Johnson’s Glass House clearly reflects his indebtedness to the work of Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, and the European modernist movement in architecture generally known as the International Style. Employing Andres Amador’s distinction, the Glass House clearly embodies a geometric conceptual basis, with the result that the building does not so much emerge from the site but instead sits upon it as an imposed human-made form. The carefully clipped and very flat lawn, and the linear walkways serve to emphasize the distinction between the structure and its natural surroundings. This leaves the Glass House appearing to be like a sculptural object that has been placed on a plaza, or like a vase on a smooth table-top, rather than as something arising from within its setting.


Brief attention to the history of these two buildings provides further insight. Wright lived at Taliesin much of his life, while also retreating to Taliesin West in the Arizona desert during the winter months. Over the years, he gathered a sizable community of apprentices who lived and worked with him at both locations. To this day, the architectural fellowship that is part of his legacy maintains both homes and studios. By contrast, though Philip Johnson first lived part-time in the Glass House himself, he soon discovered how it was largely unsuitable for that purpose, other than for entertaining guests in the living and dining areas of the structure. Given the sudden notoriety of the house, the constant presence of unwelcome visitors and architecture-minded prowlers made it problematic for every exterior surface of the house to be comprised of glass. Johnson soon made it a habit to stay in the adjacent bunker-like Brick House, designed for the site as a guest house, when spending time in New Canaan.
Obviously, it is easy to stress the marked differences between these houses designed and built by Wright and Johnson for themselves. Andres Amador’s dual approach to his earthscapes may help provide a reminder of the way that both-and thinking can aid how we consider certain objects of interest. Wright’s organic home and studio, emerging within and receiving inspiration from its site, and Johnson’s temporarily lived-in Glass House, imposed as a geometric sculpture upon its site, share a common distinction. Regardless of functional considerations, each house has its own way of displaying beauty, and both remain among a small list of internationally recognized architectural achievements of historic significance.
Note: A short introductory video about Andres Amador and his work, giving examples from both of the geometric and organic categories, introduced above, has been produced by KQED of San Francisco. It can be found on YouTube ( https://youtu.be/T_tIG5mo1DM?si=0MkjxkTEK48eC-aV ).
Taliesin East has been named a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the Glass House is a National Historic Landmark.