If reading this by email, please tap the title at the top to open your browser for the best experience. Then, clicking individual pictures will reveal higher resolution images.
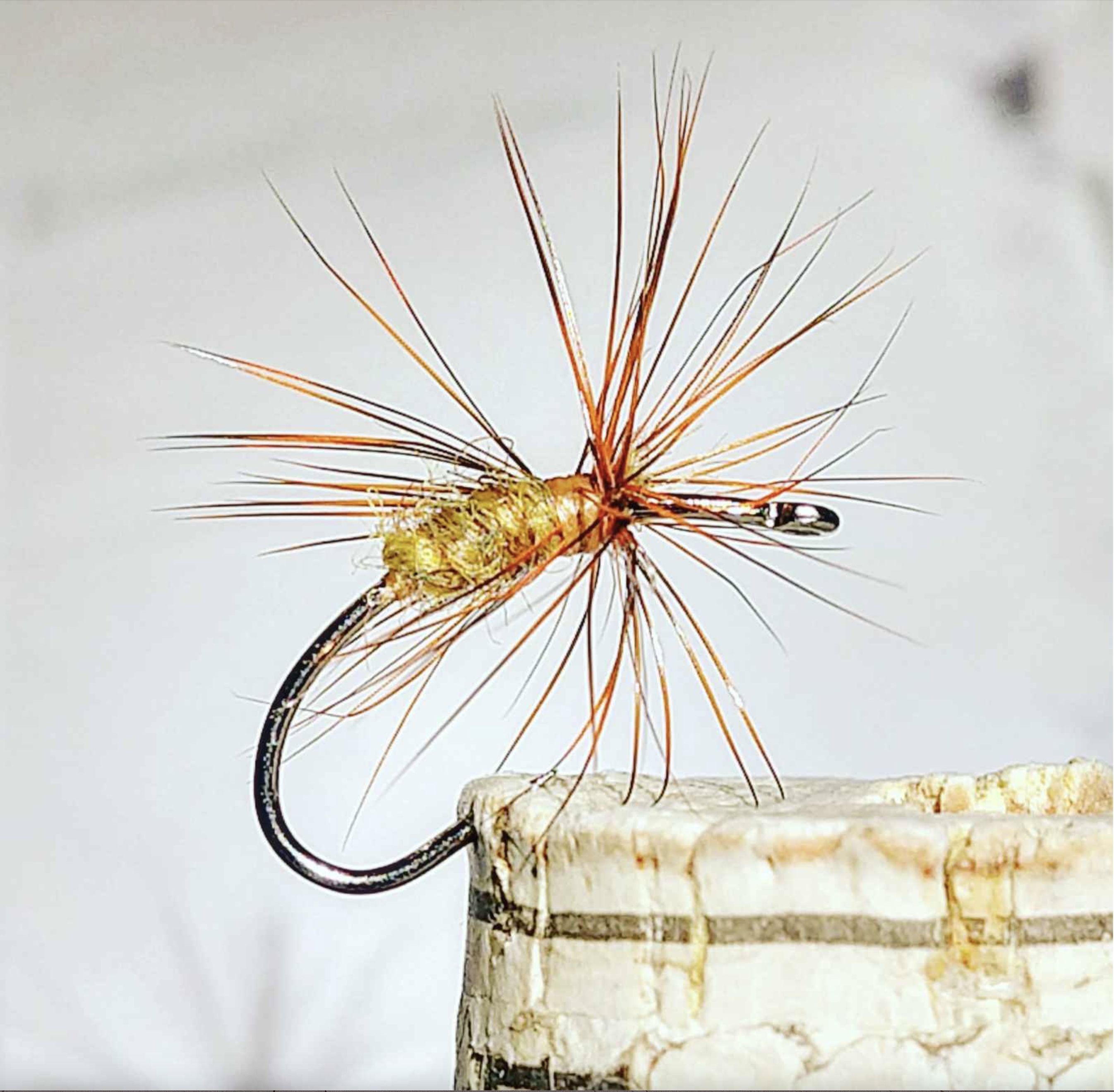
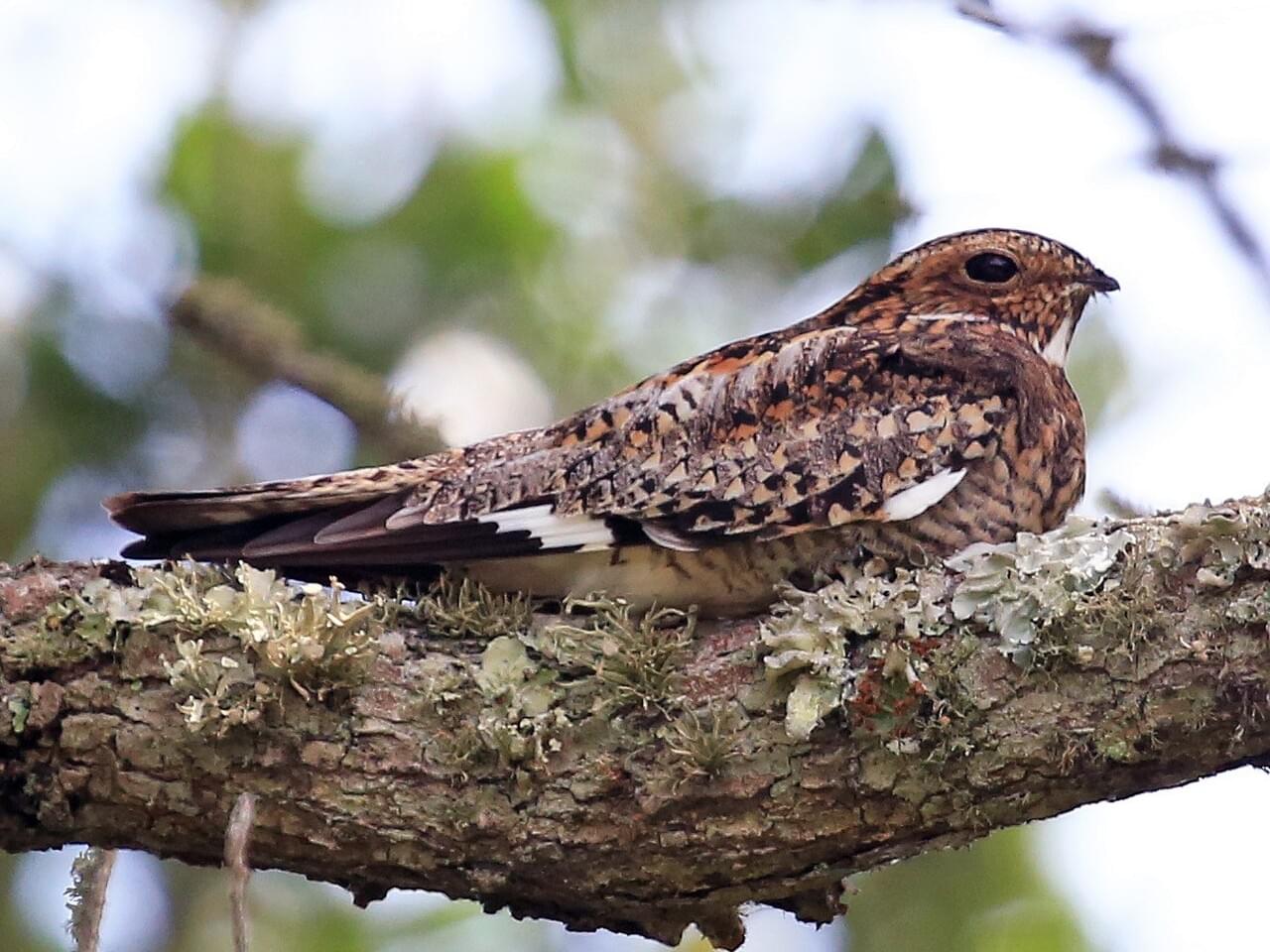
I discovered the handiwork of Jason Sparks through the writing of Jason Klass, a Colorado fisherman who has come to fish exclusively using the Japanese approach to fly fishing called Tenkara. Tenkara fishing has at least two distinguishing features, the first having to do with a difference from typical American fly fishing rods. Compared to familiar Western examples, Tenkara rods are very long poles, historically made of bamboo, along with a fixed-length line of roughly the length of the pole, and no fishing reel for the line. The flies used in Tenkara fishing are the second distinguishing feature. Tenkara flies, as in Jason Sparks’ beautiful example (above), generally feature hackle feathers (rooster and or hen) tied to the hook in a way that projects the feather’s barbs forward, toward the eye of the hook. This creates a pulsing motion when the fly is pulled against the current in a stream.
The anatomy of a fish hook. (Sparks prefers barbless hooks to facilitate ‘catch and release’ fishing)
The artistic design work of Jason Sparks, and his adaptation of traditional Tenkara flies, stress an intentional use of natural materials. In order to appreciate the originality of his flies, it’s worth considering examples of traditional Tenkara flies.
A traditional Tenkara fly tied by Dr. Hisao Ishigaki, a recognized authority on Tenkara fishing and fly tying
Traditional Tenkara flies are composed of three basic materials, a hook, thread, and part of a feather. The thread is wrapped around the neck of the hook, creating a base; thread-wraps then secure part of a feather to the hook; the feather is then spun around the shaft of the hook while perpendicular to it, thereby spreading the feather’s barbs. More thread is then wrapped around the shank of the hook, and tied off with a knot.
Almost all fly tyers make use of a vice, as depicted in the photo above, which holds the hook in place while the fly is created. One Japanese authority, Katsutoshi Amano, is famous for tying Tenkara flies without a vice:
Observing these aspects of traditional Tenkara fly design helps us appreciate Jason Sparks’ creativity and aesthetic sensibility, as he creates works of art that actually catch fish. His willingness to work beyond the usual parameters of Tenkara flies can be seen in his choice of hooks. Those employed by the two Japanese masters in the photos above feature straight shanks in the upper part of the hook.
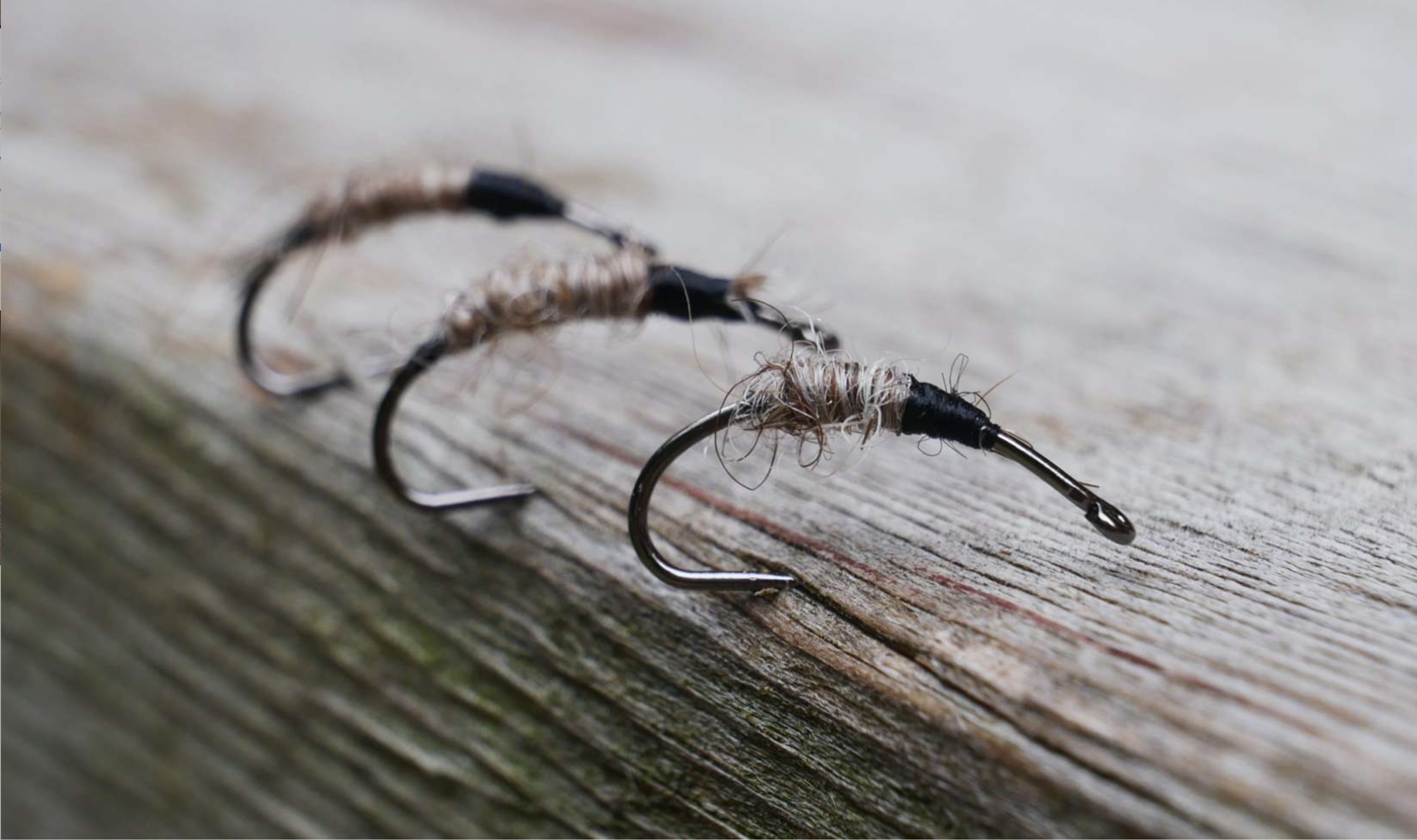
Sparks frequently uses what are commonly called scud or nymph hooks, which have a long and curving shank, where the eye of the hook tilts slightly downward. A similar tilt can be seen in another type of hook he often uses, which has a traditional straight shaft of moderate length, but which also has a wide gap above the hook’s point and a somewhat squared bend between it and the shank. These various features can be seen in photos of Sparks’ flies included below.
In both the photo directly above, as well as the one at the top, we see Sparks’ use of a scud hook, yet with minimal added material on the hook’s shank. While many tyers match fly body materials with the size of the hook, Sparks finds that a hook’s size matters less than the presentation of the material attached to it. Further, by locating that material closer to the middle of the shank, it is easier to attach or replace the fly line (and leader) to the hook’s eye.
With his preference for using natural materials, Sparks likes to tie with silk thread, and he prefers naturally dyed woolen yarn from the Shetland Islands, given its variations of color and textured finish. With a yarn ‘body,’ and the spiky feather barbs wrapped around the hook, Sparks achieves very ‘buggy-looking’ flies:
Two points are worth noting about Jason Sparks’ flies. Though the examples here look large, they are actually not very big, being photographed closely to help us appreciate their detail and composition. His typical hook sizes range from an 8 to a 12 or 14 (in most cases less than an inch, and many considerably smaller). And, second, Sparks often directs the feather barbs both forward and rearward, in contrast to the usual forward tilt of many traditional Tenkara flies. These features can also be seen in the following examples:
Sparks also ties flies that are commonly called nymphs, suggesting the appearance of bugs in their larva stage of development. With these flies, we notice the absence of feathers, and a spare use of other materials such as Sparks’ preferred Scottish yarn:
Despite how much of the hook is exposed in these examples, Sparks contends that they are effective for fishing.
Jason Sparks is obviously a gifted fly tier and has made a significant artistic contribution to this avocation, which for some is also a form of employment. In contrast to the neatness and precision of his finished flies, Sparks’ fly tying desk resembles the workspace of many others who tie flies:
Readers interested in fly tying may wish to look at my prior post, The Beauty of Fly Tying, which may be accessed by clicking here.