I have had a lifelong love of trains and of the stations where we board them. My love for them is partly inherited. My grandfather worked his whole career on the Soo Line RR, having retired as a Conductor on the overnight “Winnepeger,” running from his home in the Twin Cities to the city of the train’s namesake. And my father worked on the same railroad while in college. Of course, having spent my younger years in Japan, riding trains was an everyday occurrence.
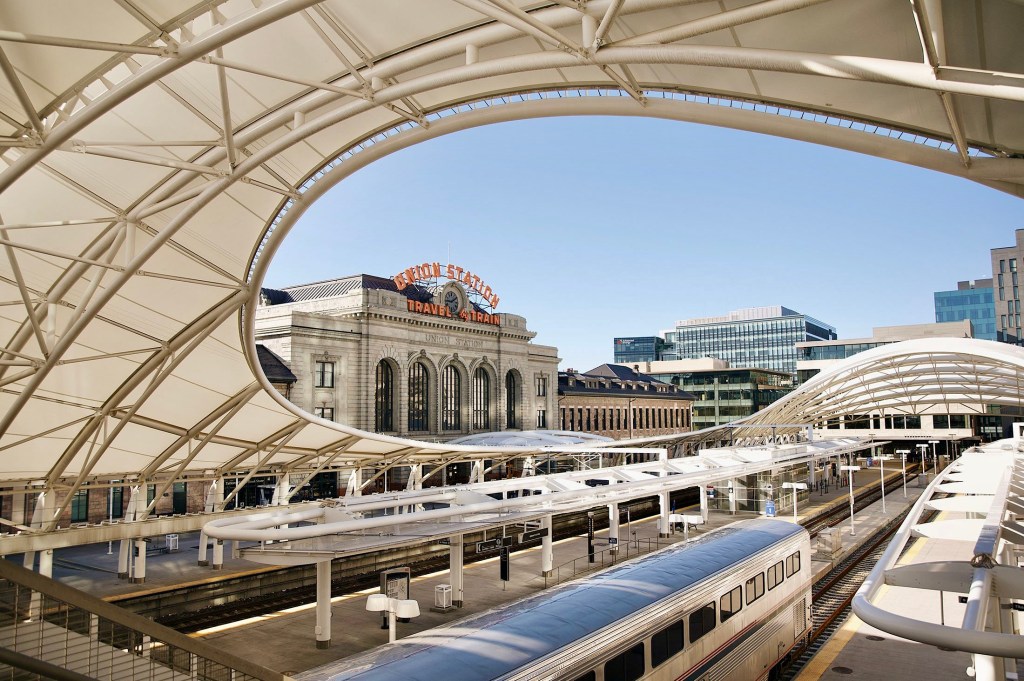
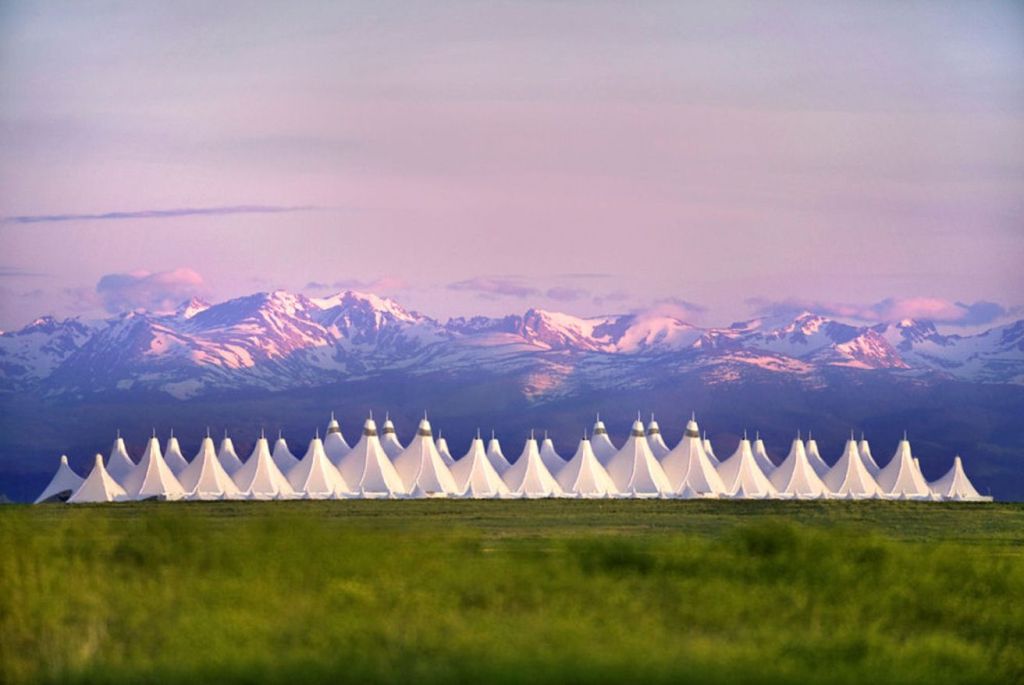
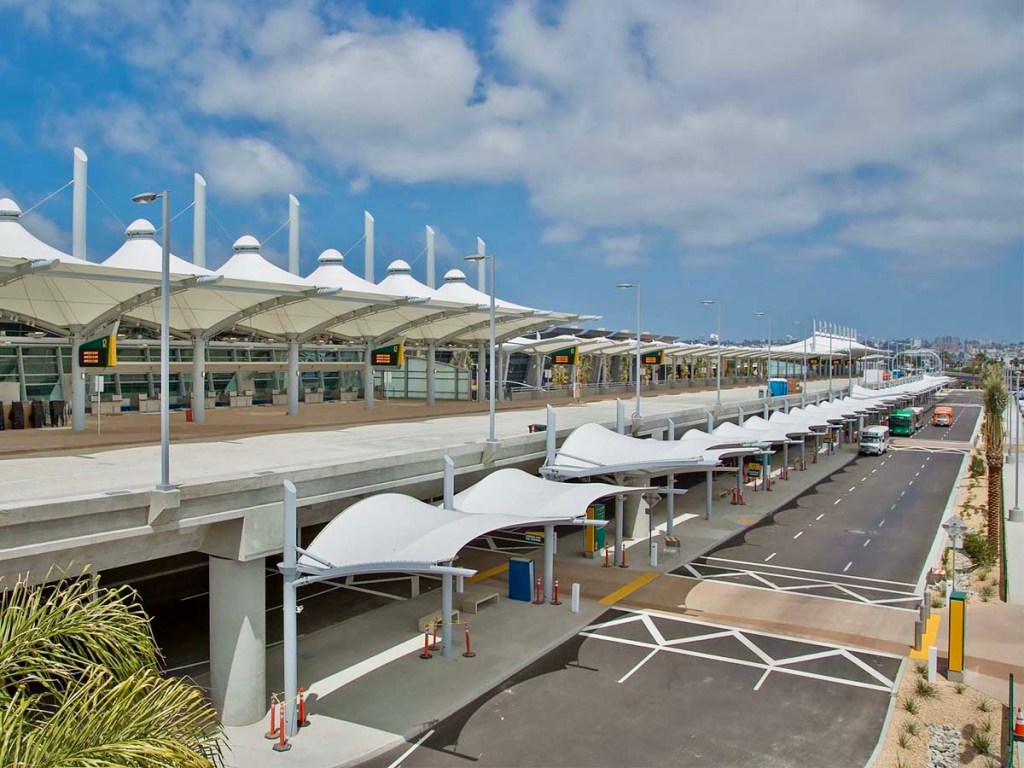
And so I am delighted this week to feature the ‘new’ (2012) open-air train shed built adjacent to Denver’s historic Union Station (now beautifully repurposed as the Crawford Hotel). What especially pleases me about the new station’s addition to the opportunities available to rail travelers in the U.S. is the apparent intention for this project to reflect a harmony with Denver’s tensile-structure airport terminal (featured in my prior post).
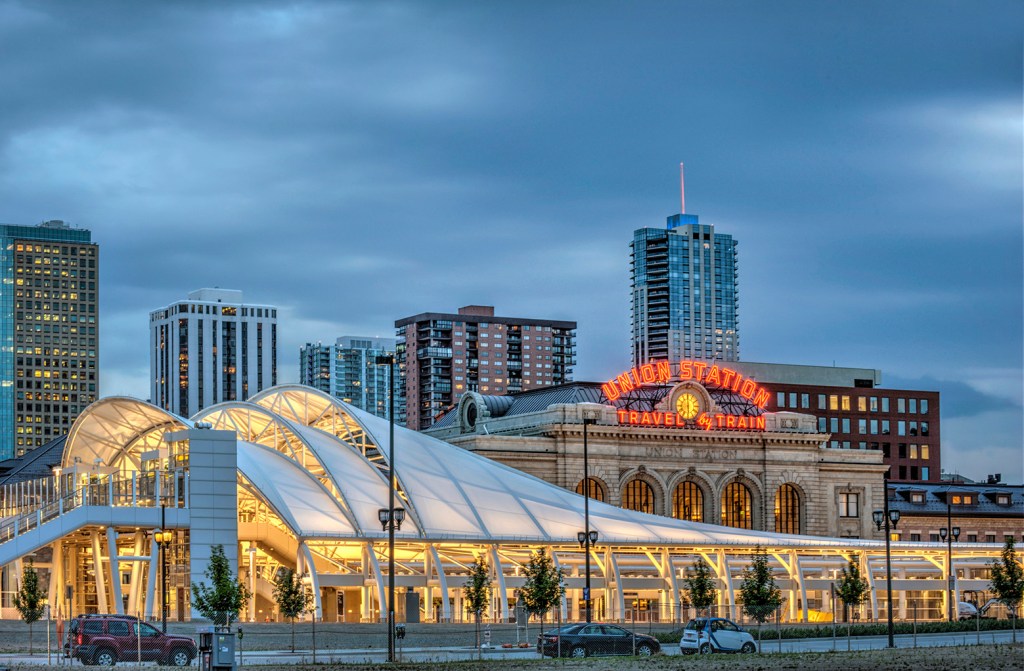


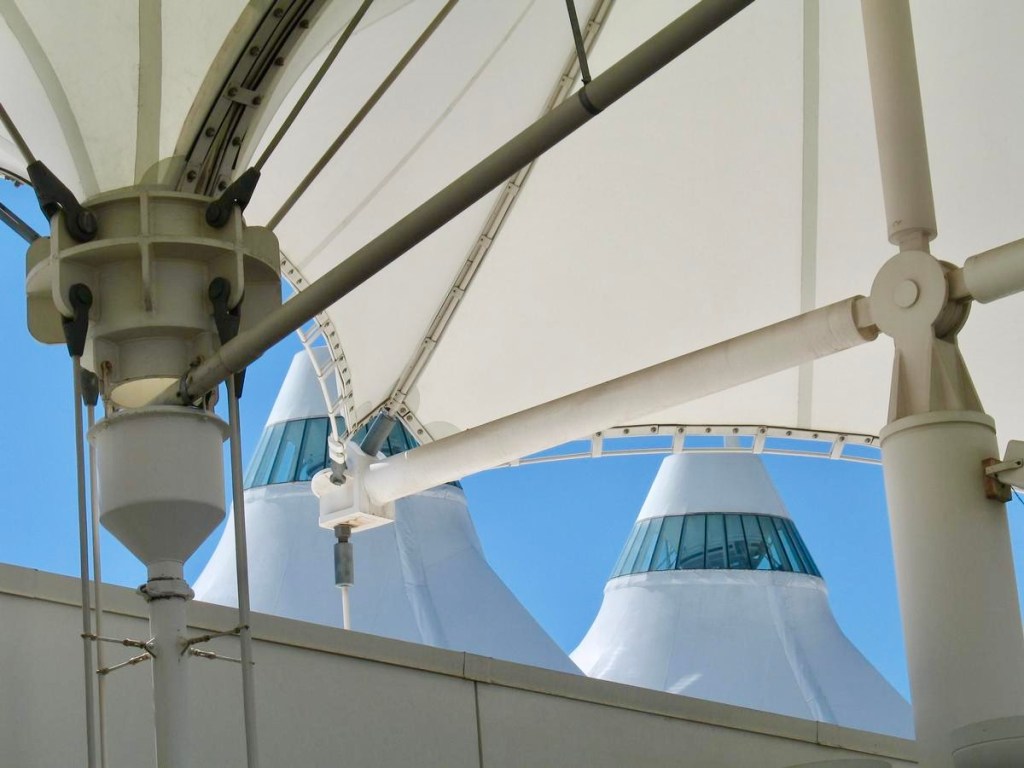
These train station platforms and their exuberant rooflines at the heart of the city, designed as part of a new transportation hub, were the creation of the long-successful and ‘big name’ architectural firm, Skidmore, Owings, and Merrill (now generally known as SOM). The awning-like structures over the platforms recall the translucent glass and steel train platform awnings familiar to rail travelers in the U.K. A difference here from the also-white structures at Denver Airport is the predominant use of steel beams as principal supports for the awnings, rather than a primary reliance upon tensile cables and poles. A greater resemblance to bridge structures results from this design choice, while also retaining the stretched fabric layers of weather protection, which like those of the airport are translucent. A lyrical building for public use once again has been provided for travelers to and within Denver.

One other significant connection between Denver Airport and the city’s new transportation hub has been established by the construction of a rail line directly linking the two. Adjacent to the tracks employed by Amtrak’s cross-country trains, Denver now has a rail line dedicated to the needs of those who wish to get to the airport, saving time as well as parking and or shuttle costs.


Denver’s new transportation hub serves as an attractive inner city renewal project, and provides a similar sense of uplift and visual ‘joy’ as does the airport. Along with the nearby 1995 Coors Field baseball park, the hub further enhances the visitor-appeal of the city’s downtown area, and serves as a central point for the region’s light rail network (RTD / Regional Transportation District).
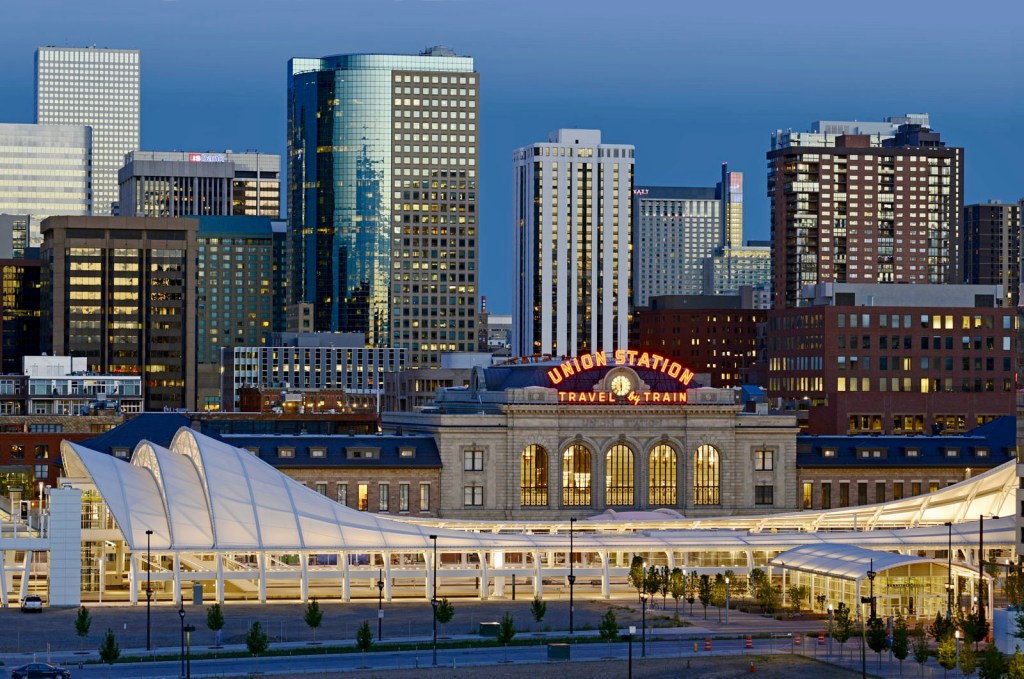

Increasingly we are recognizing the continuing implications of America’s significant distances between cities, the relatively low population density of areas between them, and how our reliance upon our cars and our expansive interstate highway system has reduced the financial viability of railroads as a primary resource for our passenger transportation needs. Nevertheless, it is pleasing to see that where new or revitalized rail stations and terminals are contemplated, there has been a demonstrated growth in awareness of their significance as public spaces not only through which we meet our travel needs, but as places where we meet and share meaningful time with others.

SOM’s Denver Station and the design of its open-air train awnings reminds me of another building, one I have loved since childhood, Kenzo Tange’s 1964 Tokyo Olympics aquatics building, which my family passed by on many family Sunday train trips to church. Tange’s employment of catenary cables for the suspension of the sweeping curved rooflines serves in a similar way as Denver Station to lift our awareness above ourselves. Design achievements like these move us to contemplate beauty as a noble goal of architecture and in engineering, a goal just as important to us as utility and efficiency.
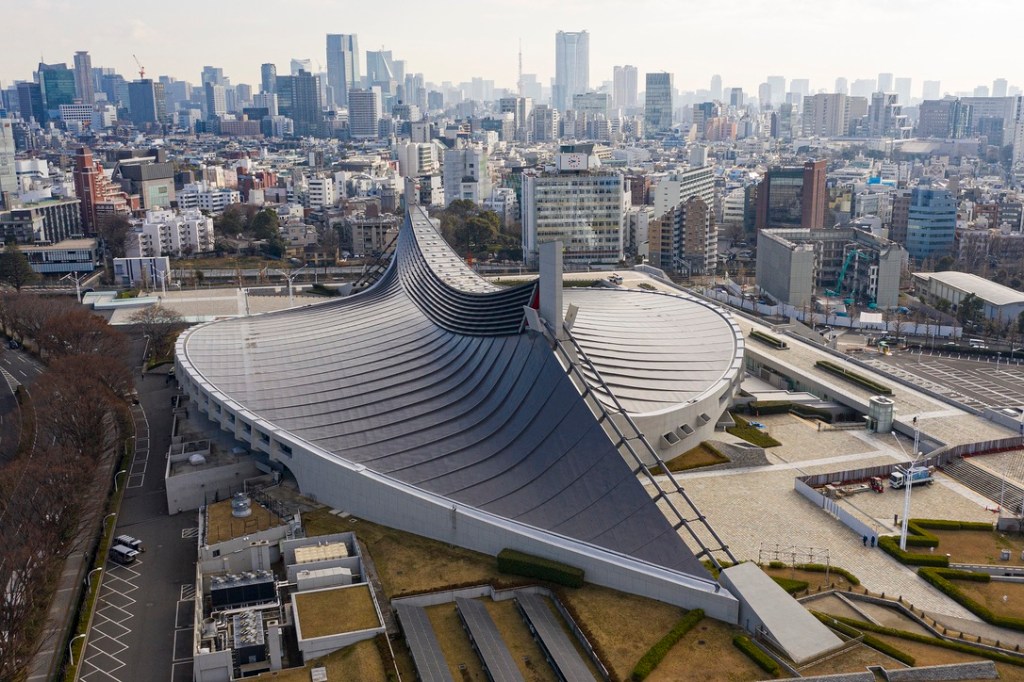


Note: My prior post featuring Tange’s Olympics aquatic center can be viewed by clicking here.